리치마작
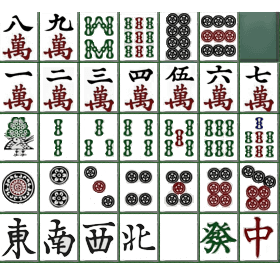 일본마작, 또는 리치마작은 전통 중국 마작이 변형된 게임입니다. 각자 패를 뽑고 버리면서 손에 패를 갖추어 화료해야 합니다. 보통은 연속된 숫자 3개나 같은 패 3개로 구성된 몸통 4개와 머리 1개의 조합을 만들게 되며, 몸통은 상대 패를 가져와서 만들 수도 있습니다.
일본마작, 또는 리치마작은 전통 중국 마작이 변형된 게임입니다. 각자 패를 뽑고 버리면서 손에 패를 갖추어 화료해야 합니다. 보통은 연속된 숫자 3개나 같은 패 3개로 구성된 몸통 4개와 머리 1개의 조합을 만들게 되며, 몸통은 상대 패를 가져와서 만들 수도 있습니다.
복잡한 점수 계산 체계와 버림패 공개가 이 게임에 깊이를 더합니다. 남의 패를 가져오지 않은 상태에서 화료하기 위해 (플레이어가 선언하고) 점수를 거는 리치도 이런 요소에 속합니다. 리치마작은 러미같은 운이 강한 손패 관리 게임의 요소를 수많은 전략과 버무렸습니다. 특히, 점수 계산 때문에 공격과 방어 모두에 통달해야 하며, 손패의 가치 분석, 패 읽기 기술, 상대의 버림패 읽기가 모두 이 게임의 승패를 좌우합니다.
리치마작은 주로 일본에서 즐기며, 프로 대국도 진행됩니다. 유럽에서는 유럽마작협회(EMA)에서 규칙과 대회를 주관하며, 보드게임 아레나에서는 2016년 기준 EMA 규칙을 따릅니다.
플레이어 수: 4
게임 시간: 42 mn
복잡성: 4 / 5
리치마작 및 다른 게임 1235개를 온라인으로 즐겨보세요.
다운로드가 필요없으며, 웹 브라우저에서 바로 플레이할 수 있습니다.
친구들과 그리고 전세계의 수많은 게이머들과.
무료.

리치마작 및 다른 게임 1235개를 온라인으로 즐겨보세요.
다운로드가 필요없으며, 웹 브라우저에서 바로 플레이할 수 있습니다.
친구들과 그리고 전세계의 수많은 게이머들과.
무료.

규칙 요약
Brief description
Japanese Mahjong is played through several hands. In each hand, the goal is to construct a valid Mahjong hand from drawn and/or claimed tiles. The set of tiles consists of three regular suits (character, bamboo, circle) and two special suits (so-called honor tiles: dragons and winds). In the regular suits there are 4x9 tiles numbered 1-9 whereas there are 4x4 wind tiles and 4x3 dragon tiles. The total number of tiles is 136. The player seats each have an associated wind direction and are rotated according to specific rules as hands are played.
To achieve a valid hand, that hand must generally consist of 4 sets and a pair. The sets can be either sequences of three tiles in the regular suits or triplets or quadruplets (three or four identical tiles) with two notable exceptions (see below). Sets can be completed by drawing tiles (regular play is in counterclockwise order) or by claiming tiles as they are being discarded by other players to form a so-called meld. Sequences can be only be called from discards made by the player to the left. Unless quadruplets occur, a hand consists of 14 (3x4 + 2) tiles and players discard down to 13. For every quadruplet, a replacement tile is drawn.
Japanese Mahjong is particular in that each valid hand must also fulfill at least one scoring condition (Yaku). These Yaku are properties of hands, and the most important ones are listed below. Different Yaku are worth different numbers of big points (Han). Secondly, the game is particular because some of the tiles (at random) are used up as so-called Dora indicators. The indicators identify tiles that will add Han to a hand, specifically the one that is next in sequence. More Dora tiles become available through forming quadruplets and through Riichi bets.
The calls for completed melds are Chi/Chii/Chow (sequence), Pon/Pong/Pung (triplet), and Kan/Kang/Kong (quadruplet). The calls to complete a winning hand are Tsumo if it is a drawn tile and Ron if it is a tile that was just discarded. A pair can only be completed from a called tile if the call is Ron. A tile that does not complete a meld or hand can never be called. Riichi is a special call that indicates that a 1000-point bet is placed. The bet is to complete a hand without altering it from this point on. It is available when the hand misses exactly one tile. The two main benefits of calling Riichi are hidden Dora tiles (also called Ura-Dora) and, most importantly, the fact that a Riichi call is a Yaku in itself.
The final value of a hand is calculated from its Yaku and sets. Unless the hand has many Han, there are also small points (Fu) that are used to compute the score.
Yaku
Some Yaku give variable Han depending on whether a hand relied on any open meld (open hand) or not (closed hand). Note that a meld-free hand completed via Ron is always considered closed, but the specific set is no longer considered concealed. For these variable Yaku, the lower number refers to open hands.
Common call-based Yaku
Riichi (1 Yaku), Ippatsu (completing hand within a single round after calling Riichi, 1 Han)
Common basic Yaku
All simples (no terminal or honor tile in any of the sets, 1 Han), no-points hand (a closed hand free of any additional Fu, 1 Han), fully concealed hand (completing a closed hand via Tsumo, 1 Han)
Common honors-based Yaku
Triplet or quadruplet of round wind, seat wind, or any dragon (1 Han each; if round wind and seat wind coincide, both count)
Common sequence-based Yaku
Identical sequences in all three suits (1 or 2 Han), duplicated sequence in the same suit (1 Han, only for closed hand)
Common terminal-based Yaku
Clean outside hand (all sets involve 1 or 9 tiles of the standard suits, 2 or 3 Han), mixed outside hand (all sets involve 1 or 9 tiles of the standard suits or honor tiles, 1 or 2 Han)
Common triplet-based Yaku
Three concealed triplets (2 Han), all-triplet hand (no sequences, 2 Han), three identical triplets in the standard suits (2 Han)
Common suit-based Yaku
Full flush (all sets from the same standard suit, 5 or 6 Han), half flush (all sets from the same standard suit or honor tiles, 2 or 3 Han)
In addition, there are rarer Yaku including the most valuable hands of them all: Yakuman hands (see below for a full list). There are two exceptions to the general structure of Mahjong hands: the first is a Yaku (2 Han) called 7 pairs, which is always a closed hand consisting of 7 different pairs. The second is a Yakuman hand called 13 orphans that consists of all 13 different terminal (1/9) and honor tiles and an additional tile from the same set of 13 tiles. Naturally, this is also always a closed hand.
Scoring
Exchange of points
If a hand is won by Tsumo, all other players pay the winner. If a hand is won by Ron, only the discarder pays the one or, rarely, more winners. The value depends on both Han and Fu unless the hand has at least 5 Han. The player sitting in the East seat (the dealer) always pays and gains more points. The other three seats are all equivalent in terms of scoring. A single round is completed after the seats have rotated once in full. However, the seats rotate only if the dealer does not win. A hand ends in a draw if no winning hand is declared before the tiles run out. The scoring in a draw is particular and depends on whether hands are declared to be what is called Tenpai (one tile away from being complete) or not. The total sum of points involved is always 3000.
The small points (Fu) are awarded to sets themselves. Sequences are worth nothing. Concealed triplets are always twice as valuable as open ones. Triplets of honor or terminal tiles are twice as valuable as triplets of common suit tiles (2-8). Quadruplets are four times as valuable as the corresponding triplets. Some Fu are given to the pair if it is a relevant wind or dragon. Finally, the base Fu of a hand are 30 (concealed hand winning by Ron), 25 (7 pairs hand), or 20 (all other cases).
Dora tiles
Anytime a quadruplet is formed, a replacement tile is drawn from the dead wall, and a new Dora indicator is revealed (unless the use of these Kan-Dora has been disabled while setting up the table). Together with the 4 replacement tiles, the Dora indicators are part of the 14-tile dead wall. One indicator is revealed at the start of each round. Each tile that is next in rank after the indicator in the same suit will count as 1 Han in a winning hand. For the standard suits, 9 wraps back to 1, for the winds, the order is ESWN, wrapping back from N to E. For dragons, the order is by Japanese alphabetical order (chun (red), haku (white), hatsu (green)), wrapping back from green to red. There can never be more than 4 quadruplets formed in a single hand, at which point all 5 Dora indicators in the top row might be visible. The ones below are the aforementioned Ura- or hidden Dora. They will be revealed only if a player who called Riichi wins a hand. This means that a maximum of 10 types of tiles could be Dora tiles. As a result, the call to form a quadruplet must be made with care. It is much safer to do so if Kan-Dora are not in use.
Strategy
Hand building
Generally speaking, Mahjong allows only drawing, discarding, and calling tiles, which means that the basic options are not complex. In Japanese Mahjong, it is frequently beneficial to keep the hand closed, that is, to refrain from forming melds through calling tiles. Because of the one-Yaku requirement, indiscriminate tile calls can easily lead to a hand that is virtually impossible to rescue. In particular, calls for sequences involving terminal tiles should be evaluated carefully. The reason is that the three simplest and most common Yaku, Riichi, all-simples, and the no-points hand, all become impossible by such a call. Building toward specific, rarer hands usually makes sense only if the hand drawn initially is well on its way towards completion. In these cases, tile calls are often essential to have a realistic chance.
Defensive play
Players begin to get an idea of the hands of other players through two main mechanisms: open melds and discarded tiles. The discarded tiles are visible for everyone and remain associated with each player. On average, the safest tiles to discard are wind tiles that are neither seat nor round wind. All honors tiles have the advantage that they play very limited roles, so the discard tableaus will give good hints if, for example, a particular dragon tile is safe to discard. In the standard suits, terminal tiles are, on average, safer to discard than central tiles because they can complete fewer sequences and because they need to be avoided for several Yaku. Later in a hand, the hopes to complete one's own hand might be so small that the priority becomes to avoid discarding tiles that lead to a Ron call. In a bad hand, it might be worthwhile to discard dangerous tiles early and hold on to safer tiles. Avoiding discards that complete hands is nearly as important as winning hands in Japanese Mahjong.
Furiten
The discard tableau plays another important role: a tile that would complete a player's hand found among the discards means that that player is in a state called Furiten. In this state, the player cannot win a hand by Ron. This rule has the very useful consequence that discarding a tile that is found in someone else's discards is always a safe defensive play against that player. Similarly, the rule means that it is unwise to change frequently the sets targeted for one's own hand. In doing so, the discard tableau will inevitably fill up with many different and unrelated tiles, which increases the chance of being Furiten and makes it easier for other players to discard tiles. Players must watch out, however, that this applies also to discarded tiles that were claimed by other players, which are consequently no longer in the discard tableau. This is why melded sets always indicate the source of the called tile by the placement of the sideways tile in the set (left: player to the left; center: player across; right: player to the right).
BGA implementation
User interface
Players can discard tiles, when it is their turn, by clicking on them. There is a player preference to turn on a confirmation button that can be useful when playing on small screens. Other options on a player's turn are buttons to form a "secret" quadruplet or an appended quadruplet. The former keeps the hand closed and is counted as a concealed set even though it is visible to other players. Finally, if the drawn tile completes a winning hand, the Tsumo button will be available. Use it to declare a win. The best scoring hand in terms of Han has to be selected according to the rules, and this is done automatically. Players do not have to denote or score hands on their own.
Whenever you discard a tile and you still have a closed hand and have not called Riichi yet, you can check the box next to Riichi close to your name and seat information. In real life, a Riichi call is done accompanying the discard and, to emphasize this, a notification is sent immediately to all players. Importantly, this only applies to a valid declaration. An invalid declaration occurs when the resultant hand is not actually one tile away from a winning hand (not in Tenpai yet). In this case, the attempted declaration will be invisible to other players and only you get a corresponding notification. Some valid Riichi calls can lead to a dead hand if the winning tiles are all used up already. This is something players have to monitor themselves. On other players' discarded tiles, buttons for tile calls or declaring a win via Ron will appear automatically. You never click directly on a discarded tile. The tile calls (Pon for a triplet, Kan for a quadruplet, and Chi for sequences) are clarified as needed in the button text itself. Passing on a Ron call puts the player at least temporarily in Furiten (permanent if Riichi was called prior).
If a game ends in an exhaustive draw, buttons appear to declare a Tenpai (hand one tile way) or Noten (anything else) hand. Sometimes both calls are eligible, and it is very rarely useful to not call Tenpai in this situation. The only downside of the call is that the hand is revealed to all players.
Tooltips explain the Dora indicators, the piles of remaining tiles (wall tiles), the bonus counter and Riichi bets on the table, as well as open tiles. The tile set itself can be changed via player preference. The "abstract" set is an original design meant to be readable universally. When a player is in the state of Furiten due to discarded tiles, the font used for the player name on the main game screen changes to highlight this. In this case, the Ron button will not show up even though the discarded tile would complete a winning hand (this is the definition of Furiten: not being able to win on a discarded tile).
Timing and automation
When setting up a table, it is possible to select options that let available calls time out. This is only available for real-time games not including training mode. It is the recommended mode in this case as it mimics what happens at a live table. Alternatively or additionally, every player has the option to set a preference to pass on some calls automatically. Note that it is generally visible to other players when this happens due to BGA's clock management, which means that it can reveal information about a hand. These options are meant primarily to facilitate turn-based play. You should understand that turning on such automation options might irritate other players. This is because the gain in information might to lead to situational advantages or disadvantages amongst your opponents.
Rule variants
Japanese Mahjong is a traditional game played in countless variants and house rules. While competition rules are increasingly standardized, the implementation offers several common variants. The webpage at https://ooyamaneko.net/mahjong/rratw/ offers a great overview of the subtle differences between various rule sets.
Alternate ending conditions
The game length can be set. Just playing the East round means that the seats need to rotate in full once. A second full rotation would be the South round. The game can end earlier if the option is selected that negative points are not allowed. In this case, the game will end immediately if a player drops below zero points. It can also last longer if the option is set that ties (for the win) must be broken. In this case, extra hands are added. As an additional non-standard mode facilitating shorter games, you can select a single-hand variant where the only condition is that that single hand must be won for the game to end immediately. Finally, the normal requirement to play repeat hands can be waived at the end of the game (known as "Agari-Yame") if the player sitting East at that point is in the lead.
Early hand terminations
So-called abortive draws can be allowed in different sets. These are special conditions upon which a hand is aborted, and new tiles are dealt. The five types are the following: three Ron calls on the same tile; fourth quadruplet formed unless they are all by the same player; four Riichi calls; four of the same wind tile discarded without interruption to start the hand; calling an aborted hand when the dealt tiles include at least 9 unique terminal or honor tiles. The last one is the only abortive draw involving player choice.
Scoring variants
The Dora tiles are a big determinant of hand scores, and they tend to be the most luck-based element in the game (especially the hidden or "Ura"-Dora). Using customization, you can increase or reduce this randomness. First, some of the 5-tiles in the standard suits can be marked red. These tiles count directly as Dora tiles and add one Han to the hand's value independent of and cumulative with the visible Dora indicators. Like all Dora tiles, they do not constitute a Yaku in itself. Red Dora tiles add an additional element of luck and volatility of scores. Second, some or all of the additional Dora indicators (except the very first one) can be removed from the game. This limits Yaku gained from Dora tiles when Kan calls have been made and when Riichi is invoked. Some competitive organizations remove all other Dora tiles, and this option is present here as well. A second more minor variant regards whether high-scoring hands (common when many Dora indicators have been revealed) that are not Yakuman hands per se should be upgraded to be counted as Yakuman hands.
Miscellaneous
The case of multiple players calling Ron on the same tile is particular. The implementation allows you to customize what happens in this case (also see the abortive draw on three Ron calls mentioned above). Finally, the starting points can be adjusted (20K, 25K, or 30K). This is of relevance only if a player dropping into negative points will actually end the game. If negative points are allowed, the number of starting points is a completely inconsequential choice.
Player preferences
While some options for player preferences are touched upon above, the following is a complete list. Because player preferences are primarily meant to change the appearance, changing them has no immediate effect despite the page reloading. The functional ones come into action only after the next user input has occurred (tile discarded or button press).
Choice of tile set
The tile set can be chosen between three variants. The "abstract" one might be better-suited for players who do not want to learn the Chinese/Japanese numerals and use small screens (so that the annotated set becomes hard to read).
Confirm choice of discarded tile
Players can request that every discard is confirmed by pressing a confirmation button. This is to prevent accidentally discarding the wrong tile, especially on touch devices.
Automatic passing
Players can set automatic passing options, which means that they will not have to press the button. When this happens, it is generally visible to other players and might reveal information about the hand although some of this is obscured by having different automatic passing options. This option exists primarily for turn-based play. For real-time play, it is preferable to use the time-based automatic passing options when setting up the game. Players should remember to change this option back to the desired state at the beginning of a hand to avoid passing on important calls.
Automatic discarding
When a player has called Riichi, the only three options on one's turn are to form a concealed Kan, to declare Tsumo, and to discard the tile just drawn. Because there is no choice of tile to discard, this process can be automated. Similarly to automatic passing, this option exists primarily for turn-based play, and players should remember to change this option back to the desired state at the beginning of a hand to avoid passing on important calls.
Animations
This player preference simply enables or disables animations of tiles moving across the board. These are implemented for the most common and important game events (drawing tiles, discarding tiles, forming melds like triplets or sequences). These animations help, especially for beginners, in understanding what the general flow of the game is. There are three options (off, fast, slow).
Custom sounds
This player preference implements a few custom, percussive sounds to be played upon special events occurring in the game (tile calls, Riichi declarations, win declarations). Each type of call is associated with a particular sound. Turning this preference on will suppress some of the default BGA sounds.
Allow reordering of tiles
Normally, the tiles are automatically sorted with a fixed order of suits and in strict numerical order within suits. For seeing some patterns, it might be helpful to rearrange the tiles slightly, and turning on this preference will create two types of buttons on the main game board under your concealed tiles: one for swapping two adjacent tiles, and one for resorting the tiles according to the standard criteria (at the far left). When tiles are removed (melds, discards), any custom order is maintained but a newly drawn tile is never sorted in. This means players are required to continuously update this order. The implementation uses clickable buttons because a drag-and-drop function might interfere too much with the process of discarding by click (or tap), i.e., lead to too many accidental discards of wrong tiles.
Additional information (not specific to this implementation or to EMA rules)
Order of play
The dealer (East) discards first, and afterwards play order is counterclockwise with the 2nd player being South, 3rd West, and the last player North. When the seats rotate after a hand has finished, they rotate in the opposite direction. East becomes North, South becomes East, and so on.
Bonus counter and bets
If a player who is not the dealer (East) wins, the bonus counter (Honba) is reset to 0; if the dealer wins, 1 Honba is added (literally a repeat). Each Honba means that payouts increase by 300 points in total. Riichi bets accumulate on the table until a player declares a winning hand. If multiple players declare a winning hand on calling the same tile, the Riichi bets are paid out only to the player nearest in turn order.
Value calculation
Once a winning hand is declared, its value must be calculated. Each Yaku gives a specific corresponding number of Han. To this, the Han from Dora tiles are added. Finally, the total number of Fu is calculated. Every hand has at least 20 Fu and 1 Han. Fu are rounded up to the nearest multiple of 10.
The base value follows with this formula: Points=fu * 2^(han+2)
The base value is replaced with a simpler table as soon as the hand has 5 Han or the value calculated above would exceed 2000 points.
If a non dealer wins by Tsumo, the dealer pays two times this base value, the others pay the value as is.
If non-dealer wins by Ron, a total of 4 times the base value has to be paid by the discarding player.
If the dealer wins by Tsumo, all other players pay twice the value.
If the dealer wins by Ron, a total of 6 times the base value has to be paid by the discarding player.
The actual payments get rounded up to the nearest 100 after multiplying as above.
1 to 4 Han: calculated as above but capped to 2000 points.
5 Han: Mangan, fixed base value of 2000 (not calculated)
6+ Han: Haneman, 3000 points base value
8+ Han: Baiman, 4000 points base value
11+ Han: Sanbaiman (lit. triple Mangan), 6000 points base value
Limit hand (Yakuman): 8000 points base value
Draws (Ryuukyoku)
Exhaustive draw
A draw occurs in the following cases, and a Honba (repeat counter, 100 point stick) is added:
If the wall has no eligible tile left, a player can either call Tsumo or discard. Likewise, after the discard, the other players get a last chance to call Ron but nothing else. If no win is declared in this way, the hands becomes an exhaustive draw.
Then depending on which players declared and revealed their hands to be Tenpai:
1 Tenpai: The Tenpai player gets 1000 from all the other players 2 Tenpai: Each Tenpai player gets 1500 from the non-Tenpai (Noten) players 3 Tenpai: The Tenpai players each get 1000 from the last player All Noten or all Tenpai: No exchange
Abortive draws (before the end of a hand) (Tochuu)
Those draws start a new hand immediately without payments, and the seats do not rotate. They are only available if the corresponding rule variant is enabled.
Nine different terminals and honors (Kyuushu (Kyuuhai))
As the name implies, the starting hand has 9 or more different terminals and honors. Calling this draw is optional.
Four winds draw (Suufon Renda (literally, four-wind repeat))
In the first turn, all 4 players discard the same round wind without interruption, that is, they "repeat" the wind.
Four quadruplets (Suukaikan)
This case only applies if multiple players have called kans, if only 1 player called all 4 kans, the player can go for a 4 kan win and hand is not aborted. In case of an open kan a final discard is required to pass (can still be ronned) before the draw is declared
Four Riichi bets (Suucha Riichi (literally 4-player Riichi))
All 4 players have called Riichi, and the last called has not been interrupted (voided) by a Ron call.
Triple Ron (Sanchahou)
3 players call Ron on the same tile discarded by the fourth player.
Detailed list of Yakus
Based on the situation of the win (1 han for most of them)
Riichi
Player has called riichi and won the hand. In this case, they get access to ura doras, a second set of dora tiles under the regular dora indicators.
Double Riichi (daburii)
Same as riichi but called on first turn before any other calls are made (1 more han than a regular riichi, therefore, double the riichi han count)
One-shot (ippatsu)
Winning on the turn a player called riichi/daburii as long as no other calls are made (so no riichi makes ippatsu not count)
Robbing a kan (chankan)
A player can rob a kan if it has been promoted from a triplet (with the exception of a certain limit hand (yakuman))
Dead-wall draw (rinshan kaihou)
If the tile a player draws after calling any kan completes their hand, this yaku is awarded.
Closed hand Tsumo (aka fully closed hand)((menzen) Tsumo)
Tsumo on a closed hand, all 14 tiles are closed in that case (closed kan is still considered closed do qualifies even though 2 tiles have their value revealed.
On draw (Haitei (raoyue))
Win on the last drawn tile from the wall
On discard(Houtei (raoyui))
Win on the last tile that would be discarded this hand
Based on hand composition
All of these amounts considered closed hand value, kuisagari means lose 1 han if open
A kan also counts as a triplet
1 han
No-points hand (Pinfu)
The hand is closed, composed entirely of runs and has it's pair already made for a 2 or 3 tile open wait, the player is not waiting on a pair with similar conditions. In this case the hand gives no fu itself.
2 identical sequences (iipei(kou))
1 set of 2 identical sequences, hand must be closed for this to count
All simples (Tanyao)
Hand is composed entirely of simples (2 to 8 in any suits) (kuitan open)
Dragon triplet (yakuhai)
A triplet of dragons (haku (white), hatsu (green), chun (red)). Note that 2 triplets stack for 2 han.
Seat/round wind (Bakaze/jikaze/kazehai)
A wind triplet fitting the round's wind or a player's seat wind. In the case it fits both, that's 2 han stack for double (wind) (dabuton, dabunan, dabusha)
2 han
Seven pairs (chiitoitsu)
The hand is composed of 7 pairs. Closed by definition, bc no pair calls exist, non-standard composition hand. gives fixed 25 fu. Not to be confused with 2 sets of identical sequences (when 2 sets of 3 pairs follow each other), which score differently.
All triplets (toitoi(tsu))
Hand is composed of 4 triplets and a pair, no value loss if open
Three color straight (sanshoku (doujun))
The same run in all 3 suits. This hand is subject to kuisagari (-1 han if open)
Three color triplets (sanshoku doukou, sandoukou)
Similar to three color straight, but this time with triplets. No value loss for opening.
Full straight (iittsuu, ikkitsukan)
The hand is composed of 123456789 in a single suit. Note that since mahjong uses only 3 tile runs, there must be 123, 456 and 789 sequences for this to count. Kuisagari applies.
Half Outside hand (Chanta(iyaochuu))
A hand composed of melds with terminals and honors. Note that a run must be present otherwise it turns into All Terminals and Honors. Subject to kuisagari
= All Terminals and Honors (Honrou(tou)) =
Like half outside but with all triplets. Note that in this case hand is at least mangan because All triplets also apply. No value loss.
Little Three Dragons (shousangen)
A triplet of 2 of the 3 dragons + a pair of the third. This hand also gets the 2 han for the 2 dragon triplets. No value loss.
Three concealed triplets (sanan(kou))
Three triplets directly in a player's hand which you haven't called, and are not part of a run themselves. No value loss.
Three quads (sankantsu)
Three quads, any work but if closed can combine with three concealed. No value loss.
3 han
Twice Double Pure Sequence (ryanpei(kou))
2 sets of identical sequences, hand must be closed. Not to be confused with 7 pairs, since highest value must always be counted.
Half Flush (honitsu)
All tiles are in a single suit and honors are present. Kuisagari applies (-1 han if open)
True Outside Hand (junchan(taiyaoo))
Like half outside, but without honors. If hand is composed of triplets, it becomes all terminals, a limit hand. Kuisagari applies(-1 han if open)
6 han
Full flush (chinitsu)
Like half flush but without honors. Like Half Flush, kuisagari applies (-1 han if open)
Limit hand
Heavenly hand (Tenhou)
Dealer has a winning hand with its initial tiles
Earthly Hand (Chihou)
Same as Tenhou, but non-dealer and no calls made
Big Three Dragons (daisangen)
A triplet of all 3 Dragons
Four Winds (suushii)
Single version: A triplet of 3 Winds + a pair of the fourth; Small Four Winds (shousuushii)
Double version: A triplet of all 4 Winds; Big Four Winds (daishushii)
Four Quads (suukantsu)
Four quads, any count. If those 4 kans are closed, this can stack with 4 concealed triplets and in this case is also pair wait for a possible triple limit.
All Green (Ryuuiisou)
Hand is composed of tiles that are entirely green (hence the name). Those are: 23468 of bamboo and the green Dragon. Not necessarily all triplets, can have a 234 run.
All honors (tsuuisou)
Hand composed entirely of honors. This hand can be 7 pairs because 7 different honors exist.
All terminals (chinroutou)
Hand composed entirely of terminals. Only available in all triplets because 6 different terminals
Thirteen orphans (kokushi (musou))
1 of each terminal and honor and a copy of one of them. If the pair is there, it's a single. (Can rob a closed kan, only case where a player can do that).
If the pair is waiting to be completed, it's a double (true or the best 13-wait kokushi).
Four concealed triplets (suuankou)
Single version: Hand is fully closed and is composed of all triplets.
Double version (suutan, suuankou tanki): 4 triplets are already in a player's hand and they are waiting for a single tile, can be ronned off of.
Nine gates (chuuren (poutou))
A hand which is composed of 1112345678999 and a copy of any tile on the same suit, Nine Gates come from the fact that hand can be completed with 9 tiles and form a valid hand. Must be closed.
Single version: A player either has all 1s or 9s of a suit in the deck or they have a pair of another number while still having the rest to get the corresponding hand, in this case single wait.
Double version (true or 9 wait nine gates): A player's hand is 1112345678999 giving you the full 9 tile wait.

